Not indexing your website in Google is equivalent to wasting your content creation efforts—your URLs (pages) would be left undiscovered by users. In this post, you’ll learn about website indexing, why it matters, and how to get your website indexed by Google.
What is website indexing?

What Is Website Indexing and How Does Google Do It?
Website indexing is the process by which search engines like Google analyze, categorize, and store the content of your website so it can appear in search results. Here’s how Google handles this process:
Crawling: Google uses a crawler known as Googlebot to find new content across the web. It discovers your site either through submitted sitemaps or by following links from already indexed pages.
Indexing: Once Googlebot accesses a page, it reviews the content—text, images, metadata, and more—to understand what the page is about. This information is then stored in Google’s massive search index.
Ranking: When someone performs a search, Google scans its index to find the most relevant, high-quality results. Pages that best match the search intent and meet quality standards are ranked higher in search results.
Google also keeps track of changes to existing content. If you update your site, Googlebot will re-crawl and re-index those changes to ensure its index remains accurate and up to date.
Why Is Getting Indexed by Google Important?
When users search on Google, the engine pulls results from its index—not directly from the live web. If your website isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in Google’s search results, no matter how valuable your content is.
Getting indexed is your entry ticket to visibility, but keep in mind: indexing alone isn’t enough. To rank well and generate organic traffic, you also need to focus on SEO best practices, including keyword optimization, content quality, user experience, and backlinks.

Here are a few less obvious benefits to getting your website indexed by Google:
- Increased visibility: With a chance to appear on Google search results, you open your website up to a massive audience who might be interested in what you have to offer.
- Organic traffic: People searching for information or products related to your website will now see it in search results. This is free, targeted traffic, unlike paid advertising, attracting potential customers who are already interested in what you offer.
- Potential for higher rankings: Getting your website indexed is the prerequisite for ranking at all. If your indexed web pages meet Google’s ranking factors, they may be able to rank higher and be visible to more people.
How to get your website indexed by Google
If your website provides good content, Google may index its pages without much hassle. The key is ensuring that Google can discover your pages and analyze what they offer.
Step 1: Create an XML Sitemap

An XML Sitemap is a file listing all the relevant URLs of your website. It provides Google with information about your website’s structure and content. Here’s how it helps your website’s indexing:
- Complete discovery: Sitemaps help search engines find your pages, ensuring that no pages are left unindexed.
- Priority signal: You can structure your sitemap in a way that highlights the most important pages, telling Google what content you consider the most valuable.
- Better efficiency: Crawling can be time-consuming. With sitemaps acting as a roadmap, Google can navigate through your website more quickly.
Read this posts from our friends at Ahrefs if you want to learn how to create an XML sitemap.
If you use a website builder like Webflow, Squarespace or Wix, you can typically find an automatically created XML sitemap in the following locations:
- yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
- yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml
Meanwhile, you can use plugins like Yoast or Rank Math to create your sitemap if you’re using WordPress (maybe this WP indexing guide is interesting for you…).
Step 2: Add your website + XML Sitemap to Google Search Console
Google Search Console (AKA Webmaster Tools) is a free tool that you can access as long as you have a website (obviously…) and a Google account (obvious as well). If you don’t have an account yet, sign up for one (HURRY UP!).
Here’s how you add your domain / website to Google Search Console:
- Go to Google Search Console and click “Start now”.
- On the upper left, click the “Main menu” (a three-lined icon).
- Expand the “Add property” drop-down and click “Add property”.
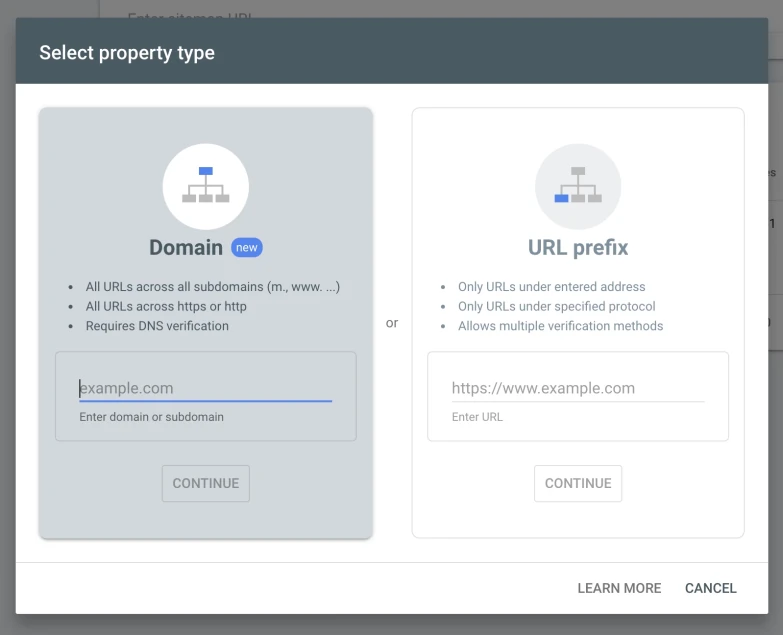
- Click “URL prefix,” enter your website URL, and click “Continue”.
- Choose a verification method of your choice and click “Verify”.
- Click “Done”.
Note: When entering the website, make sure to use its full URL prefix, such as “https://www.example.com”.
Alternatively, it is possible to add a complete domain (with all its subdomains) in Google Search Console.
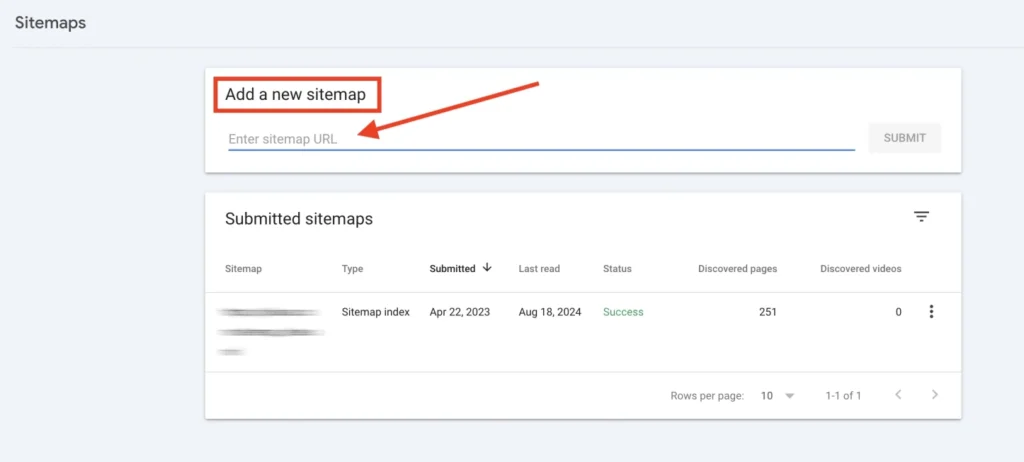
After adding your domain / website to GSC, you should add the sitemap:
Step 3: Use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console
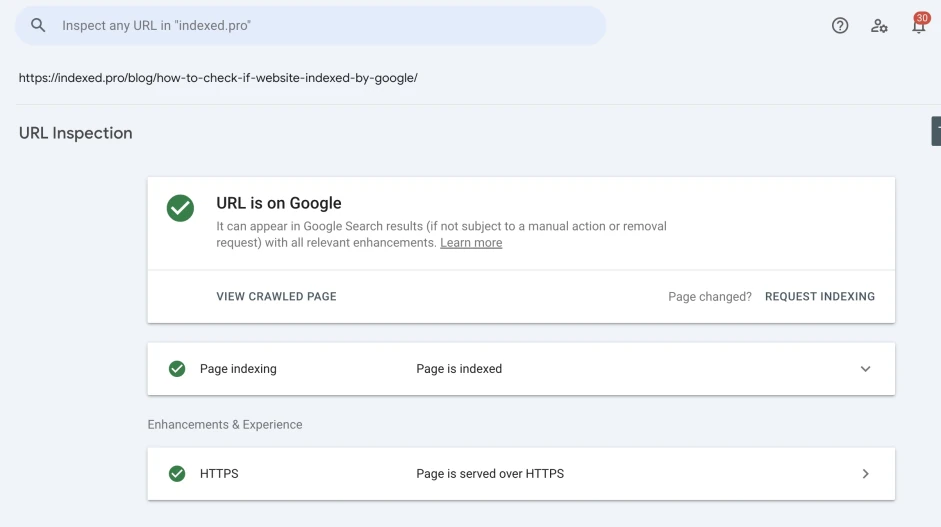
To ensure that the most important pages on your website are indexed by Google, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console. This tool lets you know about the following information:
- Indexing status: Whether the page is indexed or not.
- Crawl status: The last time Googlebot tried to access the page.
- Indexing errors: Any issues that might prevent Google from indexing the page.
- Enhancements: Information about structured data, mobile usability, and more.
Here’s how you use it:
- In GSC, click the “URL Inspection” search bar.
- Type the URL that you want to check.
- You’ll see either of the following statuses once the search is over: “URL is on Google” or “URL is not on Google”.
- If you see that the URL has not been indexed, you’ll see the reason why in the URL Inspection tool.
- Resolve the issue hindering the indexing process.
- Once resolved, go back to the URL Inspection tool and hit “Request Indexing”.
Step 4: Optimize your website for crawling (and indexing)
To enhance your website’s chances of getting indexed by Google, you must optimize it in terms of structure, content, meta information, performance, and other elements. Here are a few tips that you can follow:
Improve website hierarchy
Organize your website with a clear and logical hierarchy. This makes it easy for Googlebot to navigate through your website and understand how the web pages relate to each other.

An optimized architecture facilitates the crawling of URLs on a website and makes life easier for visitors.
Ensure quality content
Create valuable and relevant content that caters to your target audience’s needs and search intent. Search engines like Google tend to prioritize those that deliver fresh and useful content. You may be able to achieve this with:
- Incorporating a few relevant keywords to titles, headings, and texts.
- Consistent posting.
- Improving meta tags.
Improve website performance (WPO)
A website that loads fast is a website that is more easily (and economically) crawlable.
Step 5: Build high-quality backlinks

Google uses backlinks to discover new pages for indexing. When a good website links to your content, it signals Googlebot that your page exists and might be worth checking out. Backlinks also serve as votes of confidence for your site, which may help in ranking.
Here are a few ways to obtain good backlinks:
- Digital PR well done (for instance, with LinkAffinity)
- Create good content (reports, infographics, tools, guides, etc.).
- Contribute guest posts to relevant websites in your niche.
- Use your interpersonal connections in the industry.
- Create content that can replace broken links on websites that point to outdated information.
- BE CREATIVE.
Step 6: Monitor your website’s indexing status
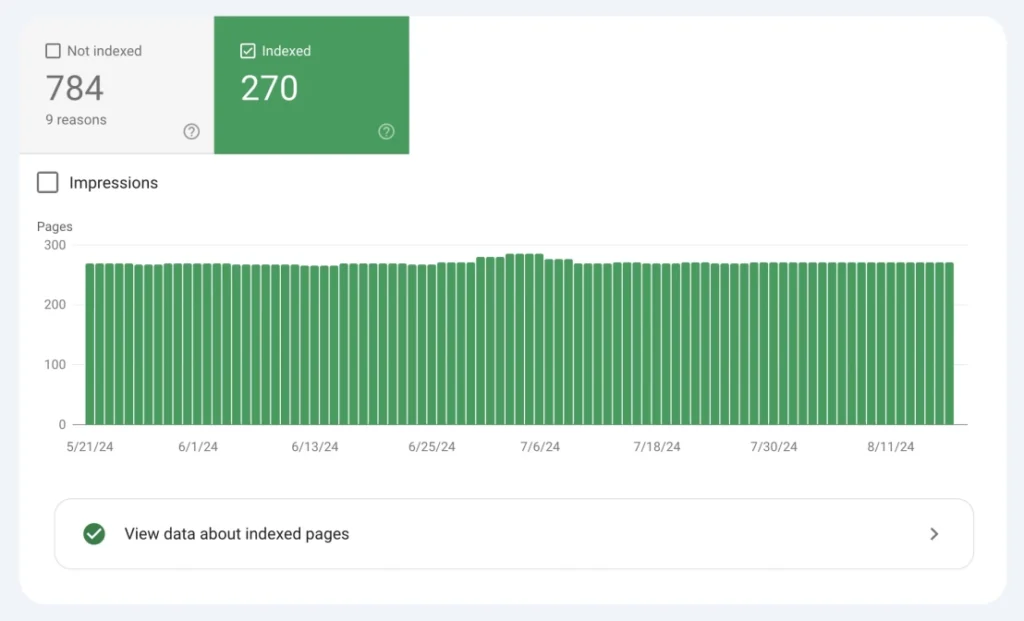
To monitor the indexing status of your website and see why some web pages are not indexed:
Step 1: In GSC, open “Main menu”.
Step 2: Under “Indexing,” click the “Pages” report.
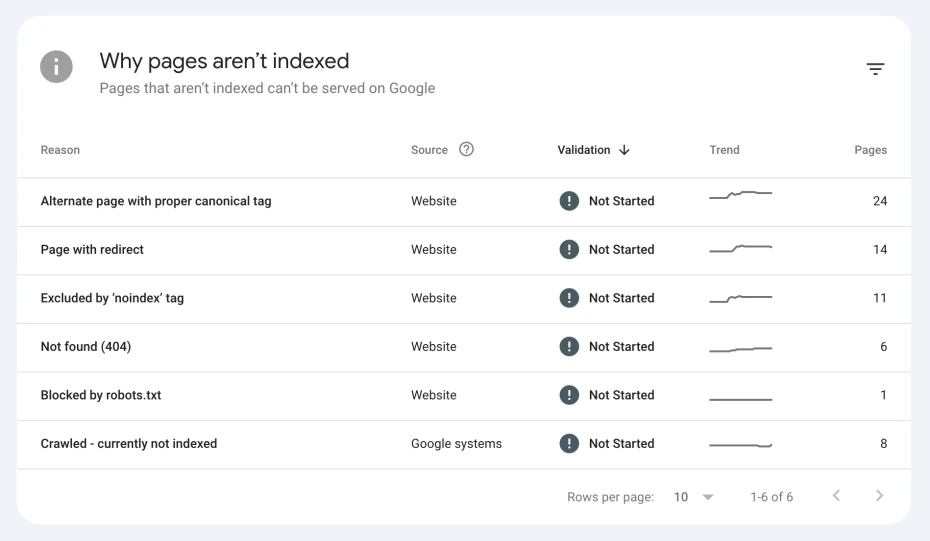
Step 3: Find the “Why pages aren’t indexed” section:
What Is Website Indexing and How Does Google Do It?
Website indexing is the process by which search engines like Google analyze, categorize, and store the content of your website so it can appear in search results. Here’s how Google handles this process:
Crawling: Google uses a crawler known as Googlebot to find new content across the web. It discovers your site either through submitted sitemaps or by following links from already indexed pages.
Indexing: Once Googlebot accesses a page, it reviews the content—text, images, metadata, and more—to understand what the page is about. This information is then stored in Google’s massive search index.
Ranking: When someone performs a search, Google scans its index to find the most relevant, high-quality results. Pages that best match the search intent and meet quality standards are ranked higher in search results.
Google also keeps track of changes to existing content. If you update your site, Googlebot will re-crawl and re-index those changes to ensure its index remains accurate and up to date.
Why Is Getting Indexed by Google Important?
When users search on Google, the engine pulls results from its index—not directly from the live web. If your website isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in Google’s search results, no matter how valuable your content is.
Getting indexed is your entry ticket to visibility, but keep in mind: indexing alone isn’t enough. To rank well and generate organic traffic, you also need to focus on SEO best practices, including keyword optimization, content quality, user experience, and backlinks.
